- : +9834-32515993
- Golomaksaze@gmail.com
Bitumen Emulsion
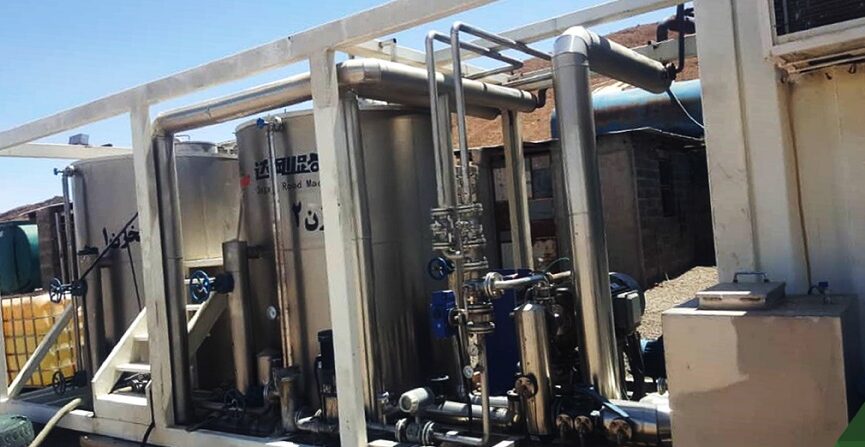

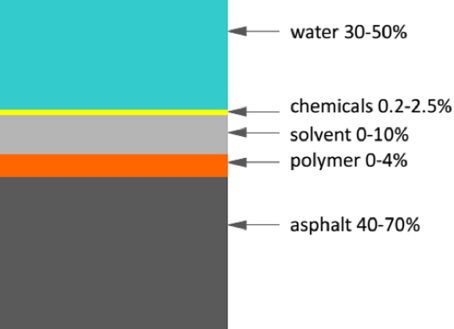
n addition to producing a variety of simple emulsion bitumens, this unit is capable of producing polymer emulsions. Currently, due to the wide range of cationic emulsifiers, different types of cationic emulsions are produced in this unit.
- Simple and polymer quick-breaking carton emulsions for single coat and chip applications
- Simple and polymeric cationic emission cations for Fog Flood and cold asphalt applications
- Simple and polymer late cation emission cations for prime coat applications and cold asphalt
- Simple and polymer fast cation emission cations for flood and microfluorescence slurry applications
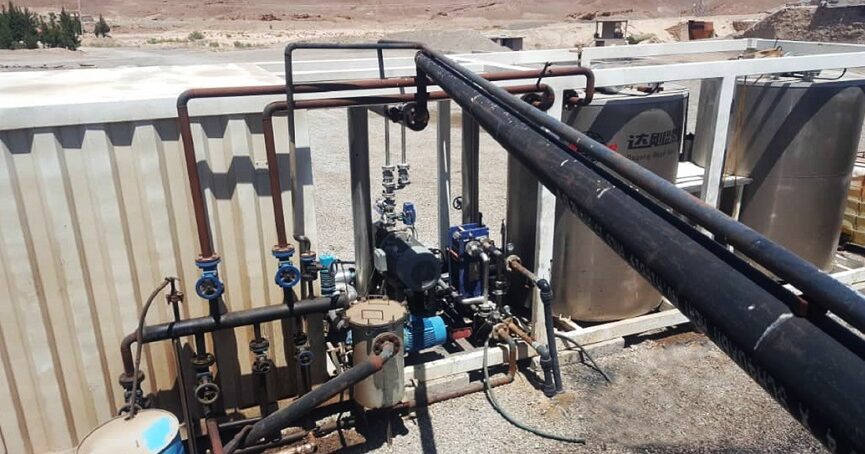

Emulsion Plant
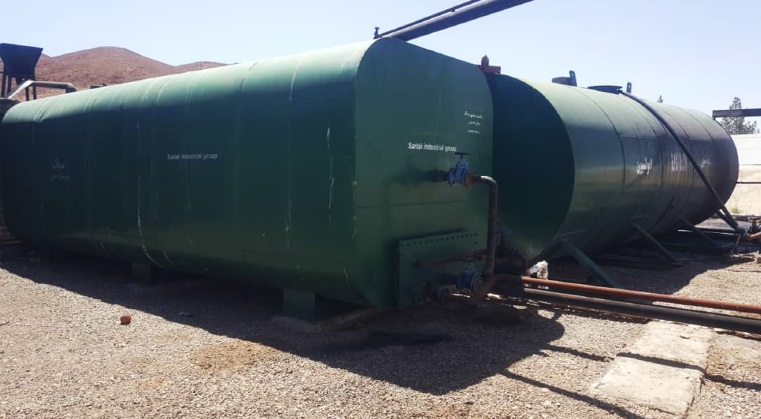

Seperate Storage Tanks
Emulsion
Applications for Bitumen Emulsion
Tack Coat
Prime Coat
Fog Seal
Cheap Seal
Cold Asphalt
Slurry Seal
Micro Surfacing
Mulching Operation
Tack Coat
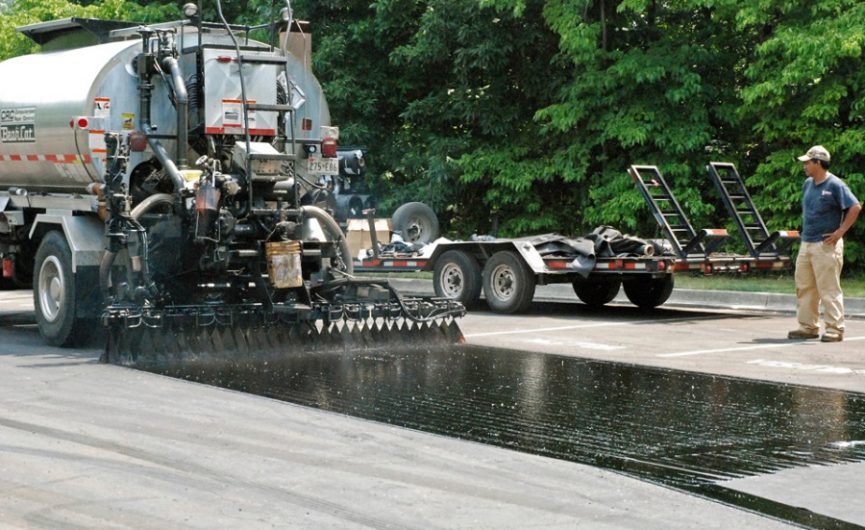
A single spread coat is a specific amount of bitumen on a relatively non-absorbent pavement surface that is applied to bond the existing surface and the new coating. A single coat is used to create the bond between the asphalt layers.
Single coat emulsion is generally sprayed at 250 to 500 grams per square meter on surfaces with different specifications. Usually, SRS1 emulsion is produced for use in single coat.


Prime Coat
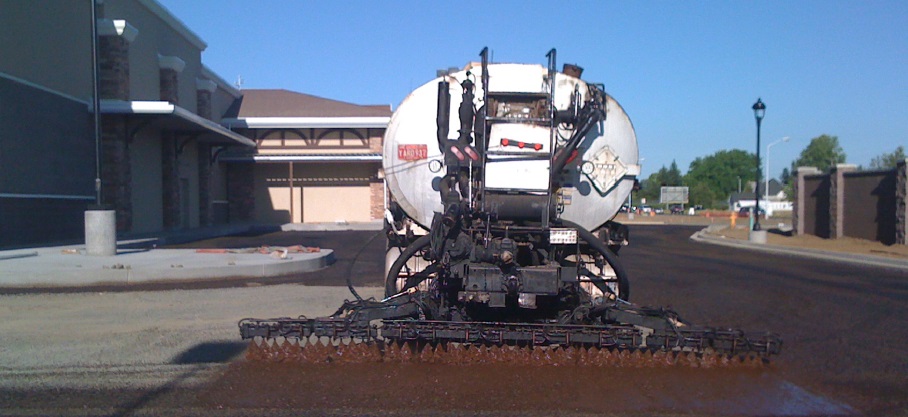
Prime Coat has a certain amount of emulsion bitumen on the adsorbent surface that is applied to penetrate the surface, stabilize the surface and the adhesion between it and the next layer.
Prime Coat is generally applied to create a bituminous layer to seal the base layer under the foundation and bed and prevents water from penetrating the lower layers. Prime coat increases the stability of the soil layer and prevents the separation of fine materials from the surface of the base layer by wind and rain. Also, the adhesion of the asphalt surface increases the base layer and prevents the thin asphalt layers on the base from slipping. Delayed cationic and anionic emulsions and the minimum amount of standard bitumen to be used as a primer coat must be high in solvent to be used without dilution and penetrate sufficiently. The emulsion consumption is recommended for prime coat is about 1.5 to 2.5 liters per square meter. The amount and size of empty spaces in the substrate material affects the permeability of the emulsion, and the type of emulsion determines the amount of section and the amount of dilution.
CSS 1 emulsion is usually produced for use in coat premiums.

Fog Seal
Fog Seal is a layer of emulsion bitumen that is sprayed on the surface and is mainly used on the existing pavement to seal small cracks, reduce bareness and improve the pavement conditions. Fog Seal is used to refresh old, dry and brittle asphalt to fill very small cracks and pavement surface cavities.
The amount of Fog Seal spread in the range of 0.45 to 0.7 liters per square meter is recommended for diluted emulsion. The surface texture of the rough pavement and the amount of cracks have an effect on the consumption of Fag Seal.
Diluted CMS 1 emulsion is commonly used for Fog Seal.

Cheap Seal(Seal Coat)
Cheap Seal is a bitumen spread on the prepared surface of asphalt sand and road concrete, on which broken and clean aggregates with the same size are immediately spread. Cheap Seal can be applied in one layer or several layers. Cheap Seal is used as a temporary pre-asphalt pavement to repair oxidation and sanding of old pavement and to create a suitable sealing surface and slip resistance. Anionic and cationic fracture emulsions with 60 to 75% bitumen are used to make Cheap Seal, and polymer bitumens are commonly used. The emulsion must have sufficient viscosity to provide the required bitumen thickness without flowing, which can be achieved by adjusting the amount of emulsion bitumen or by selecting the appropriate emulsifier. The emulsifier used has an effect on emulsion production and the final adhesion of aggregates and bitumen, and if necessary, an emulsion adhesion enhancer should be used.
CRS1 emulsion is usually used for Cheap Seal.

Cold Asphalt

Slurry Seal

Micro Surfacing

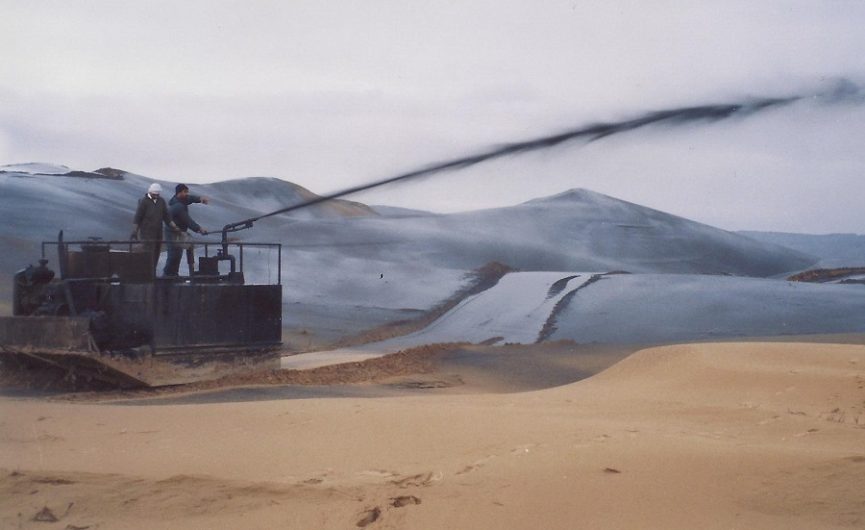
Mulching operation
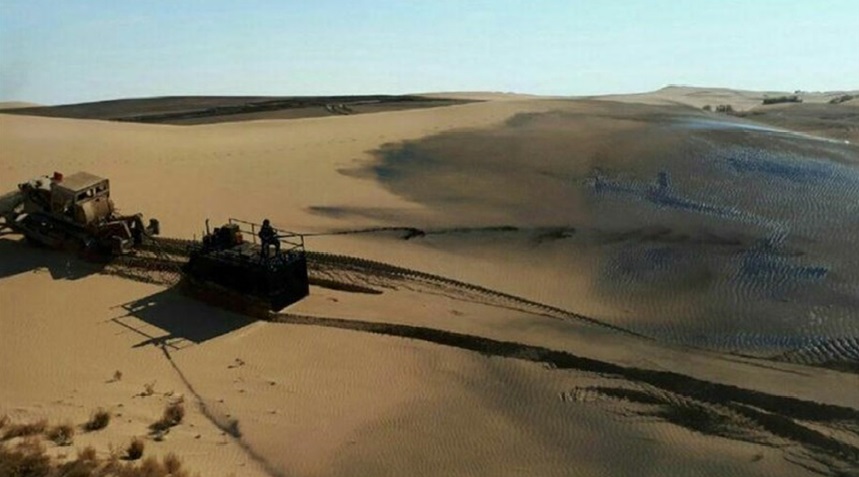

One of the applications of emulsion bitumen in the form of mulch is to stabilize flowing sand.

